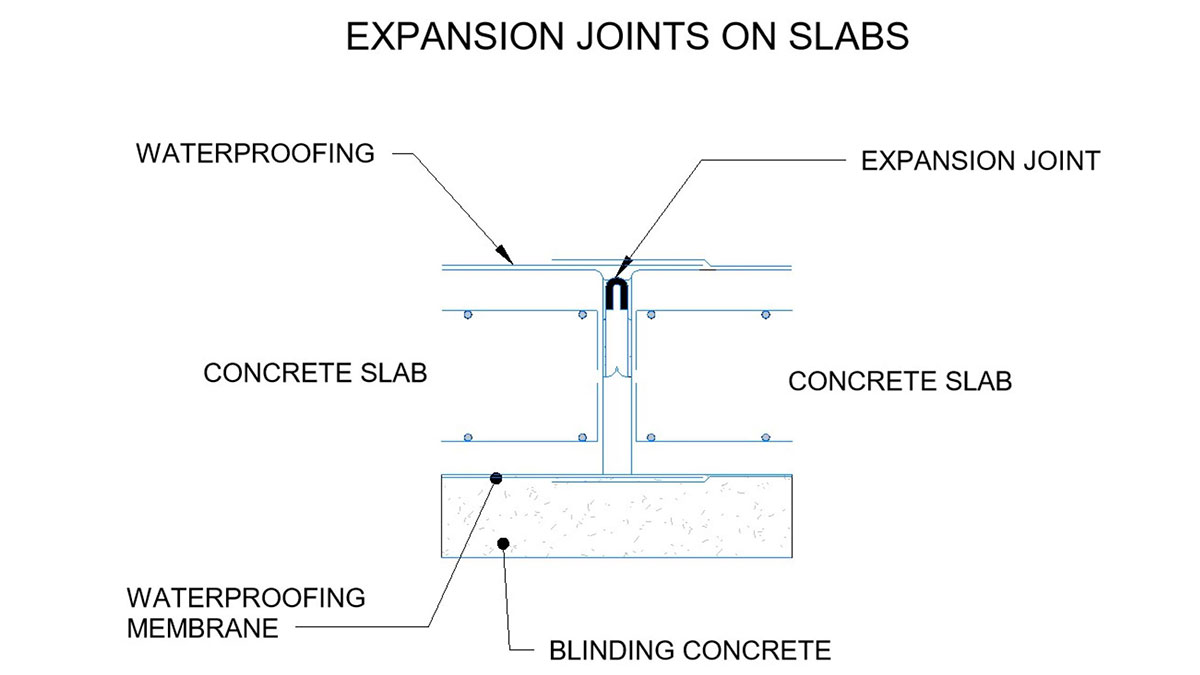
Expansion joints are strategically placed structural boundaries in the pool basin that absorb recurring expansion and contraction caused by changes in temperature, humidity, movement or other factors. In this way, expansion joints prevent cracks and damage to the pool, lengthen its life span and reduce or prevent water loss through seepage.
In the case of indoor pools, or pools built on other structures such as building terraces, etc., their expansion joints must be coordinated with the joints of such buildings or structures. The use of expansion joints should even be considered in the case of concrete construction pools.
However, there is no single formula for the location and installation of expansion joints. A specialised technical team will determine their location, distances, width, materials to be used and construction details according to the specific needs of each pool. In this regard, factors such as the size of the pool, its geometry and depth, the ambient temperature, the structural materials used and the type of support on which it is built must be taken into account.
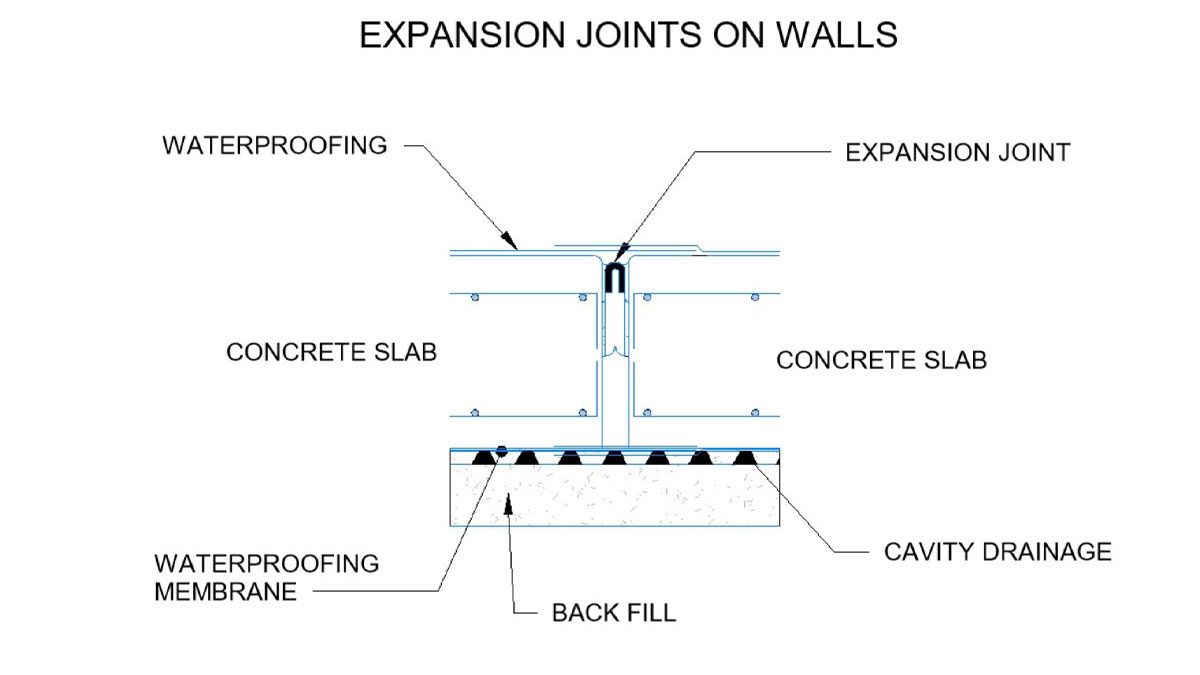

The following are the types of expansion joints available:
– Horizontal: located on the floor, they allow the horizontal expansion and contraction of the pool.
– Vertical: located on the walls, they absorb vertical movements.
– Control: they direct the cracks towards the joints.
The materials generally used for the manufacture of expansion joints are the following:
-Elastic sealants: such as silicone or polyurethane.
–Joint profiles: prefabricated to maintain the opening.
–PVC or rubber strips: these ensure waterproofing and flexibility.
Finally, it is necessary to carry out regular maintenance of the expansion joints, with the corresponding inspection, replacement of sealants or cleaning, if necessary, to ensure their correct functioning over time.
By Eduardo Hernández García, Senior Structural Modeller at Amusement Logic’s Architecture Dept.