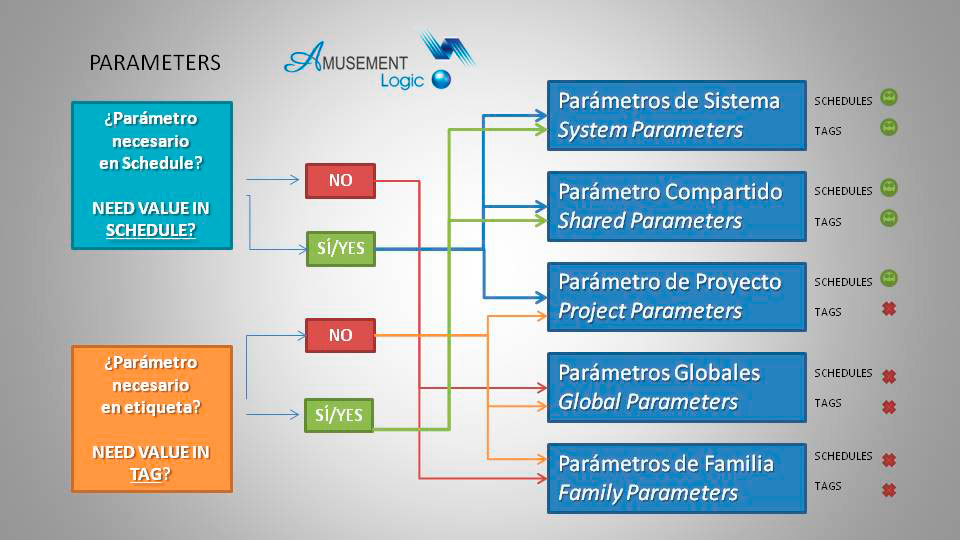
In an architectural project managed with BIM (Building Information Modelling) methodology, it is necessary to define the information of the modelled entities by means of parameters in one of the following categories:
–System parameters: predefined parameters that are used to control general elements and behaviours of the model. These parameters are integrated into the software to manage issues such as units of measurement, accuracy, annotation style, calculation formulae and other aspects that affect the project as a whole.
–Project parameters: these are created specifically for a particular architectural project. These parameters allow specific information to be stored, such as reference numbers, costs, installation dates and other relevant data.
–Family parameters: these are assigned within a family and apply to instances of that family in the model. They allow to control and modify at once the properties of the whole family, such as dimensions, materials, visibility options, etc.
–Shared parameters: especially useful when working in collaboration with other users or teams, they are created and defined in a separate file called a shared parameters file (.txt). Their advantage is that they can be used in multiple projects and families, which facilitates standardisation and the exchange of information between different files.
–Global parameters: these allow uniform and consistent values to be set throughout the project, such as regulatory constraints, which facilitates changes and adjustments to the design. These parameters are created in the parameter management interface and can be assigned to different elements of the model to control specific aspects of the design.
By David González Molina, BIM manager in the Architecture Department at Amusement Logic






